
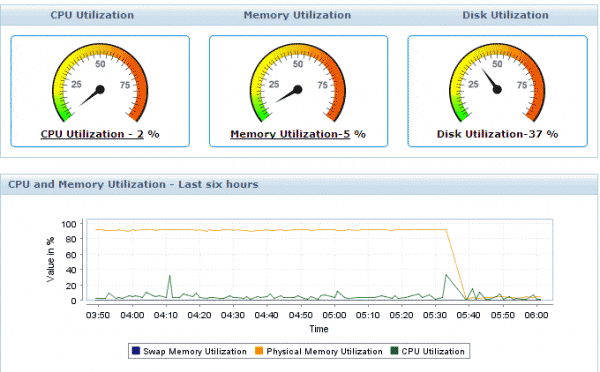
The configurations for the thresholds are stored in /etc/cumulus/nf. Systemd: Started Monitor system resources (cpu, memory, disk).Ĭumulus Linux 3.0 and later monitors CPU, memory, and disk space via sysmonitor. Systemd: Starting Monitor system resources (cpu, memory, disk)… Do not set alerts for these short bursts. Short bursts of high CPU can occur during switchd churn or routing protocol startup. When a CPU reports five high CPU alerts within a span of five minutes, an alert is logged. In addition, alerts are issued in high risk situations. usr/sbin/smond : : PSU2Fan1(PSU2 Fan): state changed from UNKNOWN to BADĬumulus Linux includes a number of ways to monitor various aspects of system data. usr/sbin/smond : : PSU1Fan1(PSU1 Fan): state changed from UNKNOWN to OK usr/sbin/smond : : Fan6(Fan Tray 3, Fan 2): state changed from UNKNOWN to OK usr/sbin/smond : : Fan5(Fan Tray 3, Fan 1): state changed from UNKNOWN to OK usr/sbin/smond : : Fan4(Fan Tray 2, Fan 2): state changed from UNKNOWN to OK usr/sbin/smond : : Fan3(Fan Tray 2, Fan 1): state changed from UNKNOWN to OK usr/sbin/smond : : Fan2(Fan Tray 1, Fan 2): state changed from UNKNOWN to OK usr/sbin/smond : : Fan1(Fan Tray 1, Fan 1): state changed from UNKNOWN to OK usr/sbin/smond : : Temp5(Board Sensor near Fan): state changed from UNKNOWN to OK usr/sbin/smond : : Temp4(Board Sensor at Front Right Corner): state changed from UNKNOWN to OK usr/sbin/smond : : Temp3(Board Sensor at Front Left Corner): state changed from UNKNOWN to OK usr/sbin/smond : : Temp2(Board Sensor Near Virtual Switch): state changed from UNKNOWN to OK usr/sbin/smond : : Temp1(Board Sensor near CPU): state changed from UNKNOWN to OK Not all switch models include a sensor for monitoring power consumption and voltage. You can also run net show system leds, which is the NCLU command equivalent of ledmgrd -d. The hardware elements and applicable commands and flags are listed in the table below. Minimum or maximum values are output depending on the flags applied to the basic command. The smond process provides monitoring functionality for various switch hardware elements. Critically high CPU use: 99% is the message.įor brevity and legibility, the timestamp and hostname have been omitted from the examples in this chapter.sysmonitor is the process that is the source of the message.For example, consider this syslog entry: T06:26:43.569681+00:00 leaf01 sysmonitor: Critically high CPU use: 99% Most log files in Cumulus Linux use a standard presentation format. Sending logs to a centralized collector, then creating alerts based on critical logs is an optimal solution for alerting. Logs are the best method to use for generating alerts when the system transitions from a stable steady state. In Cumulus Linux, rsyslog handles all logging, including local and remote logging. Triggered issues are normally sent to syslog, but can go to another log file depending on the feature. Metrics are more valuable when used for trend analysis. Examples of metrics include bytes on an interface, CPU utilization, and total number of routes.


The current version of the documentation is available If you are using the current version of Cumulus Linux, the content on this page may not be up to date. Resource Diagnostics Using cl-resource-query.Using Nutanix Prism as a Monitoring Tool.Simple Network Management Protocol - SNMP.Monitoring System Statistics and Network Traffic with sFlow.Using NCLU to Troubleshoot Your Network Configuration.Monitoring Interfaces and Transceivers Using ethtool.Understanding the cl-support Output File.Network Switch Port LED and Status LED Guidelines.Unequal Cost Multipath with BGP Link Bandwidth.Equal Cost Multipath Load Sharing - Hardware ECMP.Bidirectional Forwarding Detection - BFD.
Hybrid Cloud Connectivity with QinQ and VXLANs.Ethernet Virtual Private Network - EVPN.Virtual Router Redundancy - VRR and VRRP.Default Cumulus Linux ACL Configuration.Authentication, Authorization and Accounting.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
